
Gmail no longer just judges the content or code of your emails. It judges behavior, trust, and patterns that most senders never notice.
Your message gets blocked because Gmail’s AI monitors how you send, to whom you send, and what happens next.
When your email resembles spam patterns, even slightly, it gets flagged. Perfect authentication won’t save you if your behavior looks suspicious.
As an email deliverability consultant who has helped hundreds of brands reach the inbox successfully, I’ve prepped this guide to answer:
- Why Gmail blocks authenticated senders (and how to prove you’re not a threat)
- How complaint rates, attachment types, and subject lines play a role
- How to monitor and repair sender reputation in real-time
- What bounce codes like 550-5.7.26 actually mean
- Gmail’s strict 2024-25 enforcement rules
Let’s dive right in and figure out why your message has been blocked by Gmail (and how to fix it).
A word of advice
Avoiding Gmail blocks is just the first step. The real challenge is ensuring that your emails actually reach the inbox and drive the business results you need.
Gmail’s filtering system becomes more sophisticated every month. What worked last year might not work today. You need tools that adapt to these changes and protect your sender reputation before problems start.

With EmailWarmup.com, you get:
- Better delivery rates with constant monitoring
- Clean email lists with validation and replacement
- An email warmup that adjusts to how much you send
- Your own IP addresses to protect your sender’s reputation
- Expert help whenever you need it, with unlimited support calls
Want us to show you how it works?
Schedule your consultation call
Why does Gmail block emails in the first place?
Gmail’s filtering system protects users, not senders. Every day, it scans over 300 billion messages and blocks nearly 15 billion.
The filtering engine, powered by artificial intelligence, does more than just read your message. It watches your sending patterns, recipient behavior, and campaign timing.
When Gmail blocks your email, it’s responding to patterns it has learned from years of filtering spam, scams, and risky behavior. Your message may appear legitimate to you, but if it resembles anything suspicious, it will be flagged.
Sometimes emails with perfect authentication still get filtered. Gmail looks beyond technical setups. It checks your sending behavior, reputation, complaint rate, and campaign pace. If something feels off, the system assumes risk and acts before harm spreads.
Email deliverability is now a trust issue, instead of a server issue.
Gmail blocks senders it doesn’t trust, and that trust must be earned over time through consistent, safe behavior.
What makes Gmail block your emails?
Gmail doesn’t block randomly. It responds to specific signals, many happening behind the scenes, and even one misstep can push your domain into suspicious territory.
Understanding these triggers helps you avoid them completely.
Spammy content signals
Gmail’s filters react strongly to content that looks automated or pushy. Your message might be legitimate, but certain patterns trigger immediate suspicion.
- Missing unsubscribe links
- Messages that look automated without personalization
- Subject lines in all caps or with excessive exclamation marks
- Poor formatting (large fonts, too many images, broken HTML)
- Overuse of sales words (like “limited time,” “guaranteed,” or “urgent”)
Even harmless content can appear spammy if it follows these patterns.
You can check your content for potential spam with this email spam checker and see your spam score + percentage of emails landing in the inbox.
High bounce rates
When too many emails hit invalid or abandoned addresses, Gmail assumes you’re not maintaining your list properly. Just a bounce rate above 2% can trigger temporary blocks.
This happens because of:
- Old or purchased lists
- Mass campaigns to cold contacts
- Ignoring soft bounces (that eventually become hard bounces)
Gmail reads bounce patterns as signals of careless sending practices. That’s why you need to keep validating the emails in your list and do a hygiene check to see you’re not sending to invalid addresses.
You can use an email validation API for this purpose, or try our EmailWarmup.com to get email validation + replacement.
Authentication failures
Gmail verifies every message against three standards. Failing anyone puts you on thin ice.
- SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail)
- DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication Reporting and Conformance)
Fail one, and you’re flagged as risky. Fail all three, and Gmail will likely reject you outright with error codes like 550-5.7.26 or 554 5.7.1.
If your domain pretends to be authenticated but fails under scrutiny, Gmail treats that as spoofing. That’s a serious offense that can damage your reputation for months.
See our guide on how to setup DKIM to avoid this.
Unstable sending behavior
Sudden volume spikes raise red flags. Gmail expects gradual, consistent patterns, especially from new senders. Sending 100 emails one day and 5,000 the next looks suspicious.
Other risky behaviors include:
- Switching tools and domains frequently
- New IPs sending large volumes too quickly
- Irregular schedules (big batches followed by silence)
Consistency matters more than volume. Gmail watches for predictable, steady behavior.
Too many spam complaints
User reactions tell Gmail how to treat your future messages. Content quality matters less than recipient response.
If more than 0.3% of recipients click “Report spam,” you’re in trouble. High complaint rates lead to spam folder placement or complete blocks.
Common complaint triggers:
- Poor email list hygiene
- Misleading subject lines
- Difficult unsubscribe processes
Fixing complaints requires making emails more welcome, not just more compliant.
Technical errors that look suspicious
Some senders get blocked not because they’re spamming, but because Gmail can’t trust their technical setup. Suspicious technical issues include:
- Missing reverse DNS records
- Sending from domains without encryption (TLS)
- Using software that spoofs headers or fails to insert standard identifiers
Gmail’s filters are cautious. If your email doesn’t look structurally legitimate, it gets treated as unsafe.
What does a blocked Gmail email actually look like?
Most blocked messages don’t come with obvious warnings. They fail quietly, often without recipients knowing anything was sent. Gmail gives subtle signals if you know where to look.
Blocks manifest in different ways depending on the cause and severity.
Error messages and bounce codes
When Gmail blocks a message, your server receives a bounce reply containing specific error information. Common bounce messages include:
- 552 5.2.3 (message too large)
- 550 5.7.26 (unauthenticated sender)
- “Message blocked” or “rejected by Gmail”
- 421 4.7.0 (suspicious behavior, try again later)
These codes provide clues about the specific cause of failure.
Sudden engagement drops
Even without bouncebacks, your email statistics will shift dramatically when Gmail starts filtering you. Warning signs include:
- Replies stop completely
- Open rates suddenly drop
- Clicks vanish across multiple campaigns
If this happens only with Gmail addresses, you’re likely being filtered or blocked.
Recipients reporting missing emails
Sometimes customers tell you directly that your emails aren’t arriving. Common reports could be:
- “I never got that invoice”
- “Checked spam folder, nothing there either”
These reports indicate Gmail blocked your message before it reached any folder.
What happens when Gmail blocks your business emails?
A blocked email doesn’t just disappear. It takes the opportunity with it. The damage often goes unnoticed until sales slow, leads grow cold, or campaigns underperform for unclear reasons.
Gmail doesn’t just punish obvious spammers. It flags anyone who looks untrustworthy, even accidentally.
Your cold outreach stops working
A startup launched a targeted cold email campaign to secure demo calls with mid-sized retailers. Everything was personalized, the domain was authenticated, and open rates looked normal initially.
After three days, response rates dropped to zero. Gmail had started filtering the messages silently.
Their bounce rate was slightly above 2%, and a few recipients had marked messages as spam. The domain’s reputation sank, and within a week, every email was blocked before delivery.
The company lost three weeks of pipeline development because they didn’t notice the filtering until it was too late.
Transactional messages vanish
A small accounting firm moved to a new email provider but didn’t update its SPF or DKIM records. Invoices, client reports, and password reset emails suddenly stopped arriving.
No one was alerted about the problem. Clients just stopped replying. It took two weeks before a single customer reported that the firm’s emails were missing entirely, not in spam or the inbox.
By then, the damage was significant. Late payments, missed deadlines, and hours of manual follow-up added up to real financial loss.
Promotional campaigns crash silently
An e-commerce brand running a seasonal sale noticed that Gmail-based subscribers weren’t opening emails. Open rates on Yahoo and Outlook remained stable, but Gmail opens fell 70% overnight.
The problem was an old template with broken image links, missing unsubscribe headers, and slightly aggressive subject lines. These elements triggered Gmail’s content filters without any error messages or feedback.
When Gmail blocks your messages, there’s no visible wall, just silence. The risk isn’t rejection but complete invisibility while everything appears to be working normally.
What Gmail metrics reveal if your emails are getting through?
You can’t fix what you can’t measure. Gmail doesn’t provide a direct score, but it reacts to specific thresholds around complaint rates, bounce patterns, message structure, and sender behavior.
These signals shape how your emails are delivered or blocked.
| Metric | Recommended Target | Why It Matters |
| Spam complaint rate | < 0.1% (critical) | Gmail flags >0.3% as spammy behavior; blocks follow shortly |
| Bounce rate | < 2.0% | High bounce rates signal poor list hygiene and risky sending |
| Message authentication | Pass SPF, DKIM, DMARC | Failing any can trigger blocks or silent filtering |
| Daily send volume change | < 20% fluctuation | Spikes without a warmup look suspicious |
| Inbox placement (Gmail only) | > 85% | Lower placement often signals filtering to spam |
| Domain reputation (Postmaster) | High or Medium | “Bad” reputation leads to blocks, throttling, or spam filtering |
| TLS encryption rate | 100% (required) | Gmail treats non-encrypted email as unsafe |
What to do with these numbers
Understanding these metrics helps you spot problems before they become blocks.
- Run small campaigns first and test inbox placement using seed lists
- Use tools like EmailWarmup.com to monitor reputation, delivery errors, and complaint trends
- If bounce rates or spam complaints increase, pause sending and fix the root cause before Gmail escalates
Numbers don’t lie, and Gmail doesn’t negotiate with risk. If your metrics fall outside these targets, Gmail may treat you as a potential threat, even if your message is legitimate.
How can you stop Gmail from blocking your emails?
Gmail doesn’t want to block good senders. It needs proof that you’re one of them. Avoiding the blocklist requires consistently building trust, rather than relying on a single trick.
If Gmail can see that your messages are safe, authenticated, and well-received, it lets you through.
Authenticate everything
Set up and test all three authentication methods, as every message must pass through these checks.
- DMARC (tells Gmail what to do if SPF or DKIM fails)
- SPF (your sending domain must be authorized in DNS)
- DKIM (your messages must be cryptographically signed)
All three need to pass. Even one failure can lead to blocks or spam folder placement.
Warm up gradually
Never jump from zero to full volume, as Gmail treats sudden bursts as dangerous behavior that needs investigation

You can avoid blocks by:
- Using email warmup tools
- Starting with small batches and increasing slowly
- Maintaining steady volume without “all at once” campaigns
And warming up works for both new domains and older ones — it’s needed whenever you change ESPs, IPs, or resume sending after a pause.
Clean your list often
Inactive or invalid addresses drag your sender reputation down over time. Fix this by:
- Scrubbing lists every 60-90 days
- Removing hard bounces immediately
- Re-engaging dormant users before removing them
If Gmail sees too many bad addresses, it assumes you’re not a legitimate sender.
Avoid risky content
Your message may be clean, but the format might trigger filters. Gmail flags:
- Large or low-quality images
- Mismatched “From” addresses and domains
- Subject lines with excessive punctuation or false urgency
- Missing “List-Unsubscribe” headers (especially for bulk mail)
Use plain formatting, keep links relevant, and test emails before sending.
Lower your complaint rate
If even a small percentage of users select “Report spam,” Gmail begins filtering emails from your domain.
Prevent complaints by:
- Making your unsubscribe link obvious
- Segmenting by interest and engagement
- Not sending too often (especially to unengaged recipients)
Keep your complaint rate under 0.1% if possible. 0.3% is Gmail’s unofficial danger zone.
What should you do if Gmail is already blocking your emails?
If you’re seeing bouncebacks with phrases like “message blocked” or “unauthenticated sender,” Gmail has already flagged your domain. Fixing this isn’t instant, but it’s possible.
Recovery depends on action, patience, and proving to Gmail that the risk is gone.
Confirm the block
Start by identifying whether Gmail is really blocking your mail. Look for these signs:
- Only Gmail addresses are affected
- SMTP errors like 550 5.7.26, 421 4.7.0, or 552 5.2.3
- Recipients can’t find messages in Spam or “Filters & Blocked Addresses”
If all signs point to Gmail, stop sending temporarily to avoid making the problem worse.
Fix authentication immediately
Most Gmail blocks trace back to missing or broken authentication. Check these immediately:
- SPF (look for syntax errors or missing sending IPs)
- DMARC (avoid using p=reject while troubleshooting)
- DKIM (ensure keys are valid and aligned with the From domain)
Use tools like MXToolbox or Google’s lookup tools to verify these in real-time.
Reduce risky content
Even if your DNS is clean, Gmail may still reject based on message structure. Lower risk by:
- Removing broken image or script tags in templates
- Replacing large attachments with links (especially over 25MB)
- Simplifying subject lines (remove hype words or urgent phrases)
You don’t need to rewrite everything, just clean up what looks suspicious.
Resend carefully after changes
Once you’ve fixed the core issues, test your changes gradually.
- Start sending small batches (100-200 emails)
- Track open/click rates only for non-Gmail addresses first
- Wait 24-48 hours between batches and monitor bouncebacks
If Gmail sees steady, non-threatening behavior, it usually lifts the block without formal requests.
Monitor your recovery
Add your domain to Google Postmaster Tools and track your progress. Check these metrics:
- Encryption rate (100% TLS is expected)
- Spam complaint rate (must drop below 0.3%)
- Domain reputation (needs to move from “Bad” to at least “Medium”)
Improvement takes time. Don’t rush or revert to risky sending patterns.
Blocks are painful, but Gmail rarely shuts you out forever. The faster you fix what caused the block, the sooner Gmail will start letting your messages back in.
What are Gmail’s rules for bulk senders in 2025?
Since early 2024, Gmail has enforced tougher rules on anyone sending high volumes, especially to @gmail.com addresses.
Whether you’re running marketing campaigns or transactional flows, Gmail now expects full compliance with its standards.
Failure to meet even one requirement can get you blocked.
| Policy Area | Current Rule or Limit | Why It Matters |
| Daily message cap | 2,000 (Workspace) / 1,500 (mail-merge) | Crossing this triggers 4.7.28 Limit Exceeded errors |
| External recipient cap | 3,000 unique Gmail addresses per day | Prevents abuse and sudden spam blasts |
| Message size | ≤25 MB (including attachments) | Exceeding this causes 552 errors and total rejection |
| Headers required | Must include List-Unsubscribe + valid From | Missing headers lower trust and trigger spam placement |
| Authentication | SPF + DKIM + DMARC required | Gmail blocks unauthenticated bulk messages entirely |
| Complaint rate threshold | Must stay under 0.3% | Higher complaint rates increase filtering and eventual domain blocks |
| TLS encryption | Must use STARTTLS or equivalent | Gmail deprioritizes and filters non-encrypted mail |
| Unsubscribe accessibility | Must offer one-click unsubscribe | Gmail enforces this to reduce user friction and complaints |
So, even if you’re sending under the daily limits, Gmail still holds you to authentication and content standards.
If you’re using mail-merge, throttle aggressively and rotate IPs or domains if needed. Bulk doesn’t just mean marketing – transactional and onboarding emails count too.
Meeting these requirements is no longer optional. Gmail treats any failure as a potential risk and reacts accordingly.
What tools help you stay off Gmail’s blocklist?
You can’t guess your way into Gmail’s inbox. If you’re sending emails regularly, especially at scale, you need email deliverability software that shows you how Gmail perceives your emails.
Without them, issues like reputation dips, authentication errors, or spam complaints can go unnoticed until it’s too late.
EmailWarmup.com
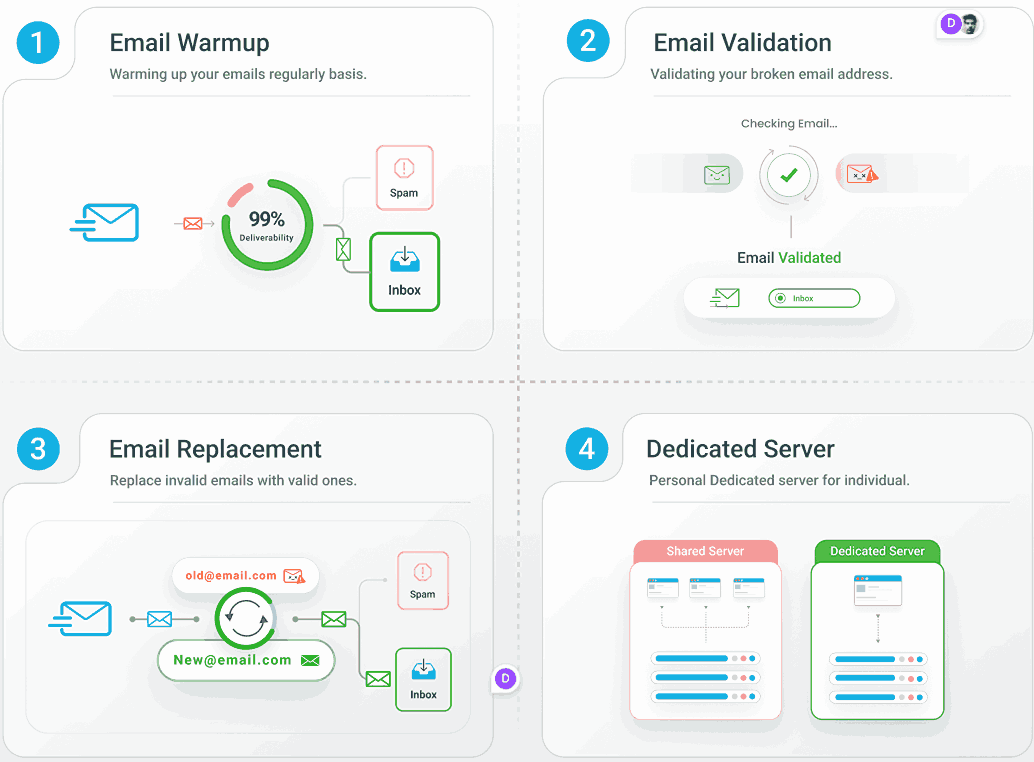
Warming up your domain is essential, and this tool automates the entire process. You’ll get:
- Inbox placement tracking across Gmail and other providers
- Gradual IP/domain warmup with daily incremental volume increases
- Live feedback on spam flags, bounce rates, and engagement health
It works silently in the background while you prepare for full-scale campaigns. This is especially critical after domain changes, new subdomains, or ESP migrations.
Seed list inbox testing
Before sending anything large, send test emails to a seed list of Gmail accounts.
This lets you check:
- Inbox vs Spam placement
- Render issues across devices
- Link tracking and header visibility
Use this every time you change templates or send to a new segment.
You can use our email deliverability checker to see where your emails land in inboxes.
Monitoring alerts for DNS and blocklists
Use tools to watch for problems before they become blocks. Monitor these continuously:
- SPF/DKIM/DMARC verification
- DNS propagation when making changes
- Blocklist appearances (Spamhaus, Google, etc.)
If you send from multiple domains, set up monitoring for each one. Gmail doesn’t just score your main brand domain.
Email deliverability is never static. Gmail’s filters adjust constantly. These tools keep you informed before small issues become delivery disasters.
How much does a Gmail block actually cost you?
When Gmail blocks your emails, it doesn’t just stop communication. It cuts off revenue.
Most businesses don’t realize it’s happening until leads dry up, follow-ups stall, or sales teams wonder why no one’s replying.
By then, the opportunity is gone.
Just a 20% drop in inbox placement can mean losing thousands in sales. One e-commerce brand lost 30% of email revenue during a campaign because Gmail silently filtered their messages.
A B2B SaaS company with a high complaint rate saw its activation emails blocked, leading to delayed onboarding and customer churn.
Email is more than a communication tool. It’s the delivery engine for your entire pipeline. If Gmail stops trusting you, that engine stalls quietly, and sometimes permanently.
The hidden costs add up quickly:
- Lost sales from prospects who never see your follow-ups
- Missed opportunities from cold outreach that never arrive
- Delayed customer onboarding when activation emails get blocked
- Damage to customer relationships when invoices or updates disappear
Fixing reputation is possible, but recovering lost revenue from missed inboxes is much harder. Prevention costs less than cleanup. Every email that reaches inboxes is a chance to grow.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions on this topic:
A blocked message is stopped before it reaches the recipient’s inbox. Gmail identifies a policy issue (possibly due to missing authentication, spam-like formatting, or a reputation problem) and rejects it outright. The sender gets an error with “Message blocked” or similar phrasing. A bounce occurs when Gmail accepts the message but later determines it to be undeliverable (such as an invalid address). You’ll get a standard “bounce-back” report instead.
Gmail changed the rules. If your message fails SPF, DKIM, and DMARC checks, appears to be spam, or triggers excessive complaints, Gmail blocks it immediately. Risky links, bad headers, or a damaged reputation can also lead to automatic rejections. To fix it, ensure that SPF, DKIM, and DMARC are passing, remove spam-trigger words and risky links, offer a clear one-click unsubscribe option, and ask recipients to check their Spam folder and mark you as “Not spam.”
Gmail considers more than 5,000 messages per day sent to @gmail.com addresses as bulk sending. Here’s what they expect:
Unique Gmail recipients: 3,000 per day
Authentication: SPF, DKIM, and DMARC required
Message size: Max 25 MB (attachments included)
Daily volume: 2,000 per user (1,500 for mail-merge)
Headers: Must have List-Unsubscribe and a valid From
Throttling, segmenting, and warming are now mandatory for any bulk sending.
Start with these steps: Check if your ‘From’ domain matches your SPF or DKIM signature. Use a DMARC checker to validate your DNS record. If you’re forwarding or using aliases, temporarily switch your DMARC policy from ‘reject’ to ‘none’. Wait a few hours after fixing – Gmail should clear the block automatically.
Gmail doesn’t offer a delisting form. Instead, address the root problem (spam, broken DNS, malware, etc.), pause sending for 24-48 hours, check if the bounceback includes a review link and submit it, and utilize EmailWarmup.com to monitor domain reputation and complaint rates.
Yes. If your total attachments exceed 25 MB, Gmail rejects the message entirely with error 552 5.2.3. Use Google Drive or cloud sharing instead of attaching large files.
Authenticate with SPF, DKIM, and DMARC and use TLS encryption; warm your IPs slowly. Ensure you keep complaint rates under 0.3% and clean your lists every 60-90 days. Also, segment large sends and test every campaign with seed lists. Consistency builds trust, and trust is what gets you into the inbox.


