
You can’t know with absolute certainty where your email landed in a specific recipient’s inbox. Email service providers don’t expose per-recipient placement data for privacy and abuse-prevention reasons.
As an email deliverability consultant who has helped businesses recover their inbox placement and conversion rates, I’ve prepared this guide that covers:
- Warning signs from engagement metrics
- The most accurate testing methods available
- Technical diagnostics that expose deliverability problems
- Why the exact folder placement remains hidden, and what you can know
While you can’t peek into every recipient’s folder, there are reliable methods to diagnose your email deliverability health before your campaigns tank.
TLDR: How to check if emails are going to spam
Here’s a breakdown of your testing options (ranked from most to least reliable).
| Method | Accuracy level | When to use it |
| Manual testing (your own accounts) | High | Before every campaign |
| EmailWarmup.com spam checker extension | High | Real-time monitoring during sends |
| Seed list testing services | Medium-high | Monthly audits |
| Engagement metrics analysis | Medium | When rates drop suddenly |
| Google Postmaster Tools | Medium | Gmail-specific reputation checks |
| Third-party spam checkers | Low-medium | Content optimization only |
How do engagement metrics reveal spam problems?
When you can’t see exact folder placement, user behavior signals become your primary diagnostic tool. ESPs monitor engagement obsessively (they use it to train their filtering algorithms), and you should too.
According to Google’s Priority Inbox research, Gmail ranks mail by the probability that users will take action. When recipients consistently ignore, delete, or report your messages, future emails face steeper filtering regardless of perfect technical authentication.
Here are some warning signs you need to look at:
Response rates tanking below 2%
Replies are the strongest intent signal and aren’t inflated by Apple opens. A drop below ~2%—especially after a 5%+ baseline—often points to inboxing issues or worn-out segments.
Open rates suddenly dropping
Treat opens as directional. Mail Privacy Protection inflates “opens,” so track changes in non-Apple cohorts and trends over time—large negative shifts suggest filtering.
CTR plummeting by provider
Big gaps between Gmail and Outlook clicks often reveal provider-specific junking or tabbing. CTR is harder to spoof than opens and highlights where filters are strictest.
Complaint rates rising above thresholds
Complaints degrade sender reputation fast. Even small, sustained increases trigger throttling and spam placement—watch per-provider spikes and make opt-outs obvious.
Understanding complaint thresholds
Gmail blocks over 15 billion spam emails daily while intercepting 100 million phishing attempts. Google’s sender guidelines explicitly state:
“Keep spam rates reported in Postmaster Tools below 0.10% and avoid ever reaching 0.30% or higher.”
Marcel Becker, Yahoo’s Senior Director of Product Management, emphasizes:
“A spam rate of 0.3% is really high. If you’re a good sender, your spam rates will be well below 0.3%.”
Here’s what these thresholds mean:
| Spam complaint rate | Status | Action required |
| Below 0.1% | Safe zone | Maintain current practices |
| 0.1% to 0.3% | Warning zone | Investigate immediately |
| Above 0.3% | Critical | Severe filtering likely |
Hard bounce rates also matter. While many sources cite bounce rates below 2% as healthy, anything above 5% signals serious list hygiene problems and triggers ESP scrutiny.
What spam rate actually measures?
There’s an important nuance here…Gmail Postmaster’s Spam Rate measures the percentage of inboxed messages that users manually mark as spam. If you bypass the inbox entirely and land in spam, that won’t inflate this metric.
A low spam rate but poor placement scenario means your emails are being filtered before reaching inboxes (where users could mark them as spam).
A sudden drop in positive responses may indicate blocklisting, reputation damage, or other technical issues. Investigate using the diagnostic tools below (and check how to stop emails going to spam for prevention strategies).
Can spam checker tools accurately predict spam placement?
Third-party spam checkers analyze your email draft and assign a spam score based on content, authentication, and technical factors. They’re helpful for pre-send optimization but come with significant limitations.
These tools check spam trigger words, DNS records (SPF (RFC 7208), DKIM (RFC 6376), DMARC (RFC 7489)), blacklist status, image-to-text ratios, and link quality (learn more about reducing spam scores). They don’t have actual data from Gmail or Outlook. Their scores reflect what might happen based on general filtering principles, not what will happen when your email hits real inboxes.
But there is an exception…
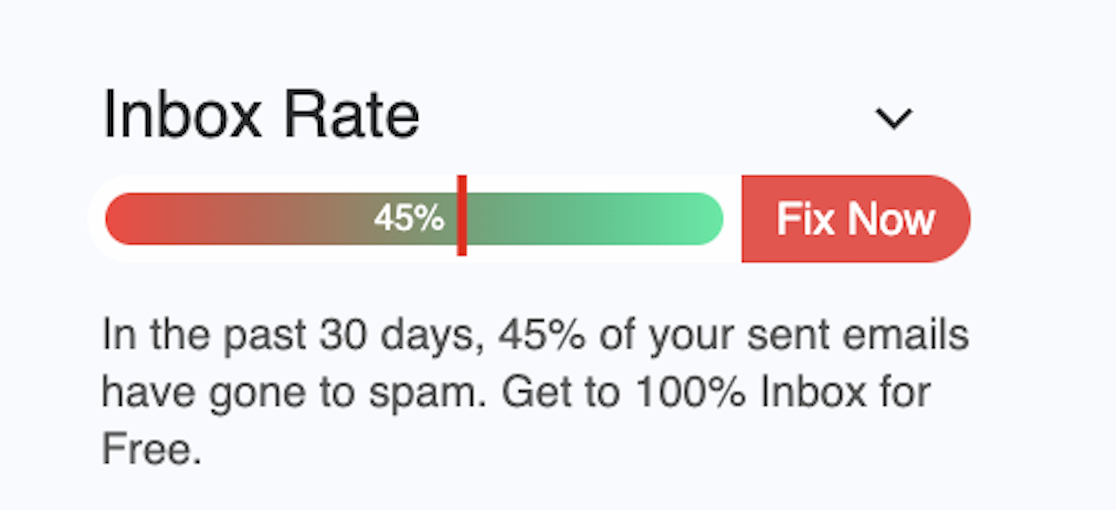
Free Email Spam Checker Extension
See exactly where your emails land (inbox, promotions, or spam) without leaving Gmail or Outlook. Get a real-time deliverability score in your compose section, and clear placement labels in your Sent folder for emails you’ve already sent. Free of cost!
Real-time deliverability score
Percentage score appears beside your compose window before you hit send.
Inbox vs. spam visibility
Instant view of what percent reached inbox vs. spam across providers.
Sent-folder placement labels
Every sent email is tagged as inbox, promotions, or spam so you actually know where your emails landed.
Unlimited & free
While other tools charge $25–$85/mo, our extension is free forever.
What technical diagnostics expose delivery issues?
Technical misconfigurations often cause instant spam filtering (they’re relatively easy to diagnose and fix).
Authentication records
Microsoft’s authentication mandate (enforced May 5, 2025) requires high-volume senders (exceeding 5,000 emails daily) to implement SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. Non-compliant emails get rejected outright with error code “550 5.7.515 Access denied.”
Missing authentication is one of the most common reasons for immediate deliverability failure (detailed setup guides: how to set up DKIM and how to set up DMARC). Verify your records using tools like MXToolbox or your ESP’s built-in verification tools. If SPF, DKIM, or DMARC are missing or misconfigured, fix them immediately.
Gmail and Yahoo also require one-click unsubscribe (RFC 8058) for bulk senders. Adding proper List-Unsubscribe headers shifts negative intent from “Report spam” to “Unsubscribe,” improving inbox placement.
Blacklist checking
If your domain or IP address appears on major blocklists, your emails get automatically filtered to spam or rejected entirely. Check if your email is blacklisted and follow the official blacklist removal instructions if you’re listed — understanding what email blacklists are helps prevent future issues.
Content and formatting red flags
ESPs flag specific content patterns:
- High image-to-text ratios
- Excessive exclamation marks or ALL CAPS
- Spam trigger words (free, guarantee, limited time, act now, discount)
- Missing unsubscribe links
- Generic URL shorteners
Engagement matters more than content. A perfectly formatted email sent to an unengaged list will still land in spam, even if recipients consistently ignore it.
How can official provider tools help?
Major ESPs offer free platforms that provide official reputation data (something third-party tools can’t access).
Google Postmaster Tools
Google Postmaster Tools provides you with direct insight into how Gmail perceives your sending domain. According to Google’s documentation, it tracks domain and IP reputation scores, spam complaint rates (percentage of emails marked as spam by users), authentication status, and delivery errors.
The limitation is that GPT only provides data for Gmail users, and it offers aggregate statistical trends rather than individual email placement (if you’re struggling specifically with Gmail going to spam, our detailed guide can help).
Microsoft SNDS and Outlook Postmaster
Microsoft’s Smart Network Data Services (SNDS) serves as the official reputation platform for Hotmail and Outlook 365 users.
SNDS provides IP-level complaint data and traffic patterns, while the Junk Mail Reporting Program (JMRP) sends you exact message copies that users junked (useful “smoking gun” evidence).
SNDS requires a dedicated IP address (making it relevant primarily for high-volume senders), but the insights it provides are authoritative and directly sourced.
Yahoo Sender Hub and Complaint Feedback Loop
Yahoo’s Sender Hub and Complaint Feedback Loop (CFL) send ARF (Abuse Reporting Format) reports tied to your DKIM domain, providing you with information on who and what was marked as spam.
When deliverability drops, checking your reputation scores across these official platforms should be your first diagnostic step — combine this with email deliverability optimization strategies for complete recovery.
Stop guessing where your emails went
You’ve spent hours crafting sequences, segmenting lists, and timing sends perfectly. Then your carefully crafted emails vanish into spam folders (and you don’t find out until your conversion rates crater).
EmailWarmup.com solves this by giving you visibility via a free email deliverability test and the infrastructure to fix your reputation permanently:
Personalized email warmup
AI-guided warmups mirror your real campaigns — curated by expert copywriters to raise inbox rates.
Email spam checker
See inbox vs spam in Gmail/Outlook with our free extension and sent-folder labels for each email.
Email deliverability test
Run unlimited tests across 50+ mailbox providers with clear inbox, promotions, and spam breakdowns.
Email deliverability consultant
Free 1:1 experts who fix SPF/DKIM/DMARC, blacklist issues, segmentation without any limits, or upsells.
Email marketing consultant
Strategy, audits, and campaign optimization to grow opens, clicks, and revenue end-to-end.
Frequently asked questions
Here are some commonly asked questions on this topic:
Spam checker tools provide educated estimates but lack access to actual ESP filtering algorithms. Manual testing with real accounts or seed list services gives more accurate results for detecting placement changes. EmailWarmup’s spam checker extension tracks your actual sent email placement.
No. If your email lands in spam, most recipients never see it. Even if they check their spam folder, tracking pixels often don’t load properly. Low open rates typically indicate spam filtering rather than disinterest.
Authentication (SPF, DKIM, DMARC) prevents spoofing but doesn’t guarantee inbox placement. ESPs prioritize engagement signals above technical setup. Sender reputation, based on how recipients interact with your emails, matters more than technical compliance.
Simple technical fixes (missing authentication records) can restore deliverability within 24-48 hours. Reputation damage requires email warmup (typically 14-30 days). Severe blacklisting may require abandoning the domain and starting fresh.
New domains face increased scrutiny because they lack a sending history and reputation. Fresh domains require a gradual warmup over several weeks before they’re ready for cold outreach. Start with low volumes (10-20 emails per day) and gradually increase them while generating positive engagement signals.
References
- IETF Datatracker. (n.d.). RFC 7489 – DMARC
- Microsoft. (n.d.). Smart Network Data Services.
- Yahoo. (n.d.). Sender best practices – Sender Hub.
- Word to the Wise. (2017). Are seed lists still relevant?
- Google Support. (n.d.). Postmaster Tools dashboards.
- Mailgun. (n.d.). How to keep your spam complaint rate low.
- Litmus. (n.d.). Apple’s Mail Privacy Protection knowledge center.
- IETF Datatracker. (n.d.). RFC 7208 – Sender Policy Framework (SPF).
- EmailToolTester. (2024). Email deliverability test results [January 2024].
- Microsoft Tech Community. (2025) Outlook’s New Requirements for High-Volume Senders.
- Google Cloud Documentation. (n.d.). Bulk mail guidelines – App Engine standard environment.
- IETF Datatracker. (n.d.). RFC 8058 – Signaling one-click functionality for list email.
- IETF Datatracker. (n.d.). RFC 6376 – DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM).
- Google Research. (n.d.). The learning behind Gmail Priority Inbox.
- Campaign Monitor. (n.d.). Making sense of email bounce rates.
- Email on Acid. (2021). The path to BIMI implementation.
- Yahoo. (n.d.). Complaint feedback loop – Sender Hub.
- Google Support. (n.d.). Email sender guidelines FAQ.
- Google Support. (n.d.). Email sender guidelines.
- Spamhaus. (n.d.). Spamhaus blocklist (SBL).


