
Your open rates just dropped 40%, your SDRs are panicking, and your VP of Revenue wants answers by Friday. It’s a pickle — you’ve tested everything from subject lines to send times, even that expensive copywriter’s templates.
Nothing works. Your emails vanish into spam while competitors fill prospects’ inboxes. Well, the problem isn’t your message — it’s your reputation.
Gmail, Outlook, and Yahoo decided you’re untrustworthy before anyone read your first word. Once that happens, even the world’s best copy can’t save your campaigns.
As an email deliverability consultant who has helped hundreds of businesses land in the inbox (instead of spam or promotion), I’ve prepped this guide to answer:
- Why IP reputation differs from domain reputation
- The real cost of reputation damage to your pipeline
- When shared IPs become a liability instead of an asset
- How Gmail treats you differently as compared to Outlook
- How to spot reputation damage before it kills your quarter
- The exact recovery process that works for marketing ops teams
Let’s dive into more detail to explore how to fix your email reputation.
If it’s too complicated, we can take care of it for you
Now, you could try figuring all this out yourself — or, if you’re a business, just schedule a free call with a deliverability consultant and let an expert take care of it.

EmailWarmup.com offers:
- Unlimited deliverability consultations
- Unlimited email warmup
- Dedicated IP address
- Email validation
We can set everything up for you right away. Want to know how?
Schedule your consultation call.
What is email reputation, and why does it control your pipeline?
Email reputation, also known as sender reputation, is a score that internet service providers (ISPs) assign to email senders to gauge their trustworthiness. Now, your reputation operates on two levels:
- Domain reputation
- IP reputation
Domain reputation
Domain reputation follows your company domain everywhere (from automated sequences to CEO emails).
IP reputation
While IP reputation depends on the specific server sending your messages (shared through SendGrid or dedicated setups).
Now, Gmail weighs domain reputation heavily, while Outlook focuses more on IP reputation. Meanwhile, Yahoo splits the difference.
So, when you’re running sequences through HubSpot, Salesforce, and your SDR tool, understanding the nuances becomes critical.
How does this reputation control your sales pipeline?
Your ESP handles IP management, but they can’t fix your domain’s reputation. So if you switch from HubSpot to Salesforce tomorrow, your domain reputation sticks with you like a shadow.
Now, ISPs don’t read your subject lines first. They check your reputation, authentication setup, and sending patterns.
If you pass their tests, your emails get delivered. If you fail, your messages disappear regardless of content quality.
The reputation system exists because spam volume is massive (we’re talking billions of messages daily).
ISPs need automated filtering to protect users, and your legitimate B2B outreach gets caught in systems designed to stop pharmacy scams.
How do you spot reputation damage before it destroys your quarter?
Your CRM dashboard might show declining performance, but the why stays hidden until you know what signals matter. Most marketing ops teams discover problems too late (after reputation damage requires weeks of recovery instead of quick fixes).
You must watch for warning patterns that appear before complete campaign failure:
- Reply rates disappearing overnight
- Postmaster Tools showing “Low” or “Bad” reputation status
- Open rates dropping below 15% (especially painful on Gmail traffic)
- Hard bounces spiking from domains that accepted your emails before
Run delivery tests before your metrics crash
Stop guessing where your emails actually land and test placement directly across major ISPs using tools that simulate real inboxes.
Send test messages to addresses that mirror your prospect’s behavior. You’ll see exactly what happens — primary inbox, promotions tab, or spam folder.
Gmail might trust you while Outlook flags everything as junk (a common scenario for B2B senders who focus on content over infrastructure).
You can do a free inbox placement test that shows exactly where your messages land before you launch campaigns (removing the guesswork that costs deals).
Do it with our free email spam checker extension and see where your emails are about to land.
It’s very important because inconsistent placement across ISPs signals reputation problems spreading through the ecosystem.
Your content triggers filters in ways you never expected
Modern spam filters analyze dozens of factors beyond obvious trigger words. “FREE” and “URGENT” are kindergarten-level detection now.
Advanced systems examine elements with machine learning precision:
- Link structures and destinations
- Authentication setup completeness
- Reply rates from previous campaigns
- Sending patterns that look automated
- Image-to-text ratios in your messages
Most ESPs include basic detection, but comprehensive analysis catches issues that compound into reputation damage over time.
You can use our email deliverability checker before hitting send (because preventing damage costs less than fixing it later).
What kills B2B email reputation faster than a security breach?
Reputation damage accelerates when marketing ops teams ignore ISP rules while scaling outbound programs under pipeline pressure.
Email providers constantly monitor for patterns indicating spam or abuse, and they punish violations quickly and forgive slowly.
Every damaged B2B program contains certain reputation killers (recognize them now or spend months in recovery mode).
Launching campaigns without proper email warmup
Sending 5,000 cold emails from fresh domains triggers every red flag ISPs monitor for spam operations. You’re essentially walking into a bank requesting a million-dollar credit with zero history.
Large volume launches cause immediate consequences:
- Rate limiting that throttles your sends
- Spam filtering that buries your messages
- Reputation penalties that stack up quickly
However, using an automated email warmup service could be helpful, as it simulates replies and folder movement.
It’s about training your ISPs to trust your domain before you launch full campaigns. The solution requires patience, which most B2B teams hate.
If you’re doing it DIY, start with 50-100 emails daily from new domains and increase gradually over 4-6 weeks — let ISPs observe normal engagement patterns.
Now, most companies rush under quarterly pressure (understandable when deals are on the line), but rushing costs months of recovery time when reputation crashes.
List quality problems that poison domain reputation
Your lists might include hidden dangers that damage your reputation immediately.
Invalid emails
Email spam traps exist specifically to catch bad senders, and invalid emails generate hard bounces that signal poor list management to ISPs monitoring your behavior.
Role-based addresses
Role-based addresses (info@, sales@, support@) rarely convert but frequently cause problems.
When you send to contacts like support@bigcompany.com, you’re essentially emailing a black hole that ISPs know doesn’t represent real engagement.
High bounce rates and spam complaints follow immediately when you email the wrong people.
Therefore, it’s very important to do email list hygiene before sending to addresses that could taint your email reputation permanently.
You can use an email validation API to remove bad addresses.
Ensure that you clean every list through email validation before sending anything.
Authentication setup that fails in subtle ways
Email authentication proves your identity to ISPs through SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records. Configure any piece incorrectly, and you’re broadcasting that your emails can’t be trusted (even when everything else looks legitimate).
SPF
SPF records declare which mail servers can send for your domain. Too restrictive settings block legitimate emails from your ESP. Too permissive settings let spammers abuse your domain.
DKIM
DKIM adds digital signatures proving email integrity during transit. Private keys must match your ESP setup precisely.
DMARC
DMARC ties SPF and DKIM together while instructing ISPs on what to do when authentication fails.
Set it to “reject” without proper testing, and you’ll block your own legitimate emails. Leave it at “none” forever, and ISPs assume you don’t care about security.
Hence, even minor configuration errors trigger authentication failures that compound over time.
Sending patterns shouldn’t look automated
ISPs deploy sophisticated detection systems specifically designed to catch bot-like behavior that indicates spam operations.
Your sequences trigger red flags when they show patterns like:
- Identical send times across large batches
- Obvious personalization that fools nobody
- Duplicate subject lines that look templated
- Volume spikes when someone decides to “catch up” on outreach
Natural sending looks different. Timing varies like human behavior (people don’t send emails at exactly 9:00 AM every day). And personalization has depth beyond “Hi {{FirstName}}” replacement. Volumes stay consistent day-to-day rather than spiking randomly.
Also, multiple domains sending identical content simultaneously signal coordinated spam operations. If you use different domains for different campaigns, warm each one separately with unique content and timing patterns.
Why does Gmail filter your emails differently from Outlook?
Each major ISP uses completely different algorithms and priorities for filtering decisions.
Gmail emphasizes engagement above everything
Gmail tracks opens, clicks, replies, and folder movements to dynamically determine sender reputation. Their machine learning systems adapt rapidly based on user behavior patterns.
So, high engagement rates improve your Gmail reputation quickly, and low engagement kills it faster than other ISPs because their algorithms respond to user signals in real-time.
Also, Gmail’s promotions tab isn’t necessarily death for B2B senders. Many professionals check it regularly (especially when they’re researching solutions).
But spam folder placement becomes nearly impossible to recover from without significant reputation repair work.
Outlook focuses on technical factors
Microsoft’s filtering system (covering Outlook, Hotmail, and Live) weighs technical elements heavily:
- IP reputation scores
- Authentication compliance
- Historical performance data
- Sending pattern consistency
Content filtering tends to be more predictable than Gmail’s machine learning approach.
Technical fixes work more reliably for Outlook delivery issues (which is why authentication problems hurt Microsoft delivery more than Gmail).
Yahoo and Apple Mail fall somewhere between
Yahoo emphasizes domain reputation while responding well to a proper authentication setup.
Yahoo users tend to be less engaged than Gmail users, which affects your metrics but doesn’t necessarily indicate filtering problems.
Now, Apple Mail filters based on user behavior and device-specific signals. They respect other ISP filtering decisions but maintain independent systems.
So, you might see different placement rates across devices. Here’s what you need to do:
- Prioritize technical setup perfection for Outlook
- Focus on engagement optimization for Gmail success
- Maintain a consistent domain reputation across all platforms
How do you actually repair a damaged reputation?
Reputation recovery requires a systematic approach over 4-8 weeks with consistent execution. Quick fixes don’t exist, but proven processes deliver predictable results when followed properly.
However, a word of caution.
Start with an accurate diagnosis before attempting any repairs because wrong fixes waste precious time and potentially damage reputation further (like trying to fix electrical problems without turning off the power first).
1. Clean your database completely
Your contact database contains reputation poison that must be removed before attempting recovery.
Skip cleaning, and you’ll restart the recovery process multiple times (wasting weeks when pipeline pressure is high). Get rid of:
- Role-based emails that hurt engagement
- Contacts who haven’t engaged in 90+ days
- Invalid addresses flagged by validation tools
- Obvious spam traps with suspicious patterns
Also, check for spam trap indicators that most validation tools miss.
Emails with typos in major domains look suspicious. Pattern emails (like abc123@domain.com sequences) raise red flags.
Moreover, addresses from known trap domains exist specifically to catch bad senders.
Therefore, you should export your bounce list from the past six months and cross-reference it with your current database.
Be sure to remove persistent problem addresses permanently because they’ll keep damaging your reputation every time you send.
2. Fix authentication completely
Properly configured SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records become non-negotiable requirements for reputation recovery.
Your SPF record should include your ESP’s authorized servers with appropriate mechanisms.
End with “-all” (hard fail) or “~all” (soft fail) depending on your confidence level, and avoid too many DNS lookups that cause authentication failures.
DKIM requires coordination with your ESP through their specific interface to generate domain keys through their dashboard.
Add the public key to your DNS records and verify the signature validates correctly across multiple email clients. DMARC starts with a monitoring policy (“p=none”) while you verify that authentication works correctly across your entire email ecosystem.
Graduate to “p=quarantine” then “p=reject” as confidence builds through successful authentication reports.
3. Restart with minimal volumes
Begin sending to your most engaged contacts in small batches that prove your legitimacy to ISPs watching your behavior patterns.
Follow a proven recovery schedule:
- Week 1: 50-100 emails daily to contacts who opened/clicked in the past 30 days
- Week 2: Increase by 25-50% as metrics stabilize
- Week 3-4: Continue gradual increases based on performance
- Week 5-6: Approach normal volumes if all signals remain positive
Don’t rush under pipeline pressure from leadership.
Reputation recovery takes time regardless of business urgency or quarterly goals (rushing just extends the timeline when you have to restart).
So you should focus on content that generates replies during recovery phases — questions, surveys, and valuable resources encourage engagement that signals legitimacy to ISP filtering systems.
Monitor and maintain ongoing
Reputation monitoring becomes an ongoing operational requirement rather than a one-time project that you can forget about after recovery.
Weekly reporting should include email deliverability rates by ISP, bounce and complaint trends, authentication status, and blacklist status.
Monthly analysis examines engagement patterns and reputation score trends to catch gradual degradation before it becomes crisis mode.
Now with EmailWarmup.com, you get your hands on real-time monitoring of your reputation scores, blacklist status, and authentication health through their live dashboard.
Their 50,000+ inbox network continuously maintains positive engagement signals even after you reach full sending volume (so your reputation doesn’t decay when you focus on other priorities).
What results should you expect during reputation recovery?
Successful reputation recovery shows measurable improvements within 2-4 weeks of proper execution.
Complete recovery takes longer, but you’ll see positive momentum early when following proven processes. The timeline depends on damage severity and the consistency of your recovery process execution.
Here are some things you can look for:
1. Early indicators appear first
Your ESP’s analytics improve before your email metrics show a change.
Bounce rates stabilize below 2% as ISPs accept your emails again. Moreover, spam complaints drop toward zero with better targeting.
Also, authentication failures decrease to under 1% and blacklist appearances clear up with delisting requests.
Email performance follows reputation improvements
Performance metrics show predictable patterns.
So your open rates typically recover to 20%+ as inbox placement improves and reply rates increase naturally when decision-makers actually see your messages.
The click-through rates improve as engaged contacts receive relevant content.
Eventually, your messages escape spam folders and start reaching promotions tabs, then primary inboxes.
Full recovery to pre-damage performance levels requires 6-8 weeks of consistent execution without shortcuts.
Companies that rush the process or skip steps end up restarting recovery multiple times (extending the total timeline significantly when deals are waiting).
Track the metrics that actually matter
Your standard email analytics don’t reveal the complete reputation story that determines your success. Monitor additional signals that predict future performance:
- Blacklist appearances (maintain zero tolerance)
- Authentication failure rates (should stay under 1%)
- Inbox placement percentages by ISP (test monthly)
- ESP throttling messages (should disappear as reputation improves)
Segment performance analysis by ISP to identify platform-specific issues requiring different approaches.
Gmail recovery might outpace Outlook performance, or vice versa, depending on your specific reputation problems.
When should marketing ops teams get professional help?
Most reputation damage requires specialist intervention beyond typical marketing ops capabilities. The technical complexity and time sensitivity make DIY approaches risky for pipeline-dependent businesses operating under quarterly pressure.
Professional consultation makes sense when you see warning patterns:
- Multiple ISPs show a poor reputation simultaneously
- Business impact exceeds potential consulting investment
- Deliverability problems persist after implementing basic fixes
- Technical setup requires expertise beyond your team’s capabilities
Quality email deliverability consultants diagnose your specific situation rather than providing generic advice that applies to everyone.
They’ll identify subtle configuration errors, list quality issues, and sending pattern problems that automated tools consistently miss.
Your domain might have historical reputation damage from previous marketing efforts. SPF records might contain subtle errors that most validation tools can’t detect properly.
List hygiene might need advanced segmentation beyond basic email validation services.
Are you going through something like this? You can get on a call (free of cost) with an email deliverability consultant who has years of experience under their belt — with battle-tested strategies and tips to help you out (in your specific situation).
Questions to separate qualified experts from generalists
Ask specific questions to identify consultants who understand B2B SaaS email deliverability:
- What ongoing monitoring do you recommend after recovery completion?
- How do you diagnose domain versus IP reputation issues in our situation?
- What’s your typical timeline for reputation recovery with similar tech stacks?
- Can you provide references from companies with comparable sending volumes?
- What’s your experience with our specific ESP and B2B SaaS reputation recovery?
Qualified consultants ask detailed questions about your current setup, sending volumes, and business requirements before proposing specific solutions. They should understand your CRM integration, ESP configuration, and current authentication setup intimately.
Make sure you avoid consultants promising overnight fixes or guaranteeing specific open rate improvements.
Why do most B2B companies get reputation wrong?
The most common mistakes companies make while understanding email reputation involve:
Treating email like any other marketing channel
The biggest mistake marketing ops teams make is treating email like other marketing channels, where you can A/B test your way out of problems or simply increase volume to improve results.
Email deliverability operates on trust signals that build slowly over time through consistent behavior. ISPs prioritize user protection over your business needs without exception.
They would rather block 100 legitimate emails than allow one spam message through to their users — most companies discover reputation problems too late in the damage cycle.
By the time open rates drop dramatically, domain reputation damage requires weeks of systematic recovery work.
Therefore, prevention costs less than cure (especially when deals are on the line and every qualified lead matters).
Thinking ESPs take care of everything
The second critical mistake is assuming your ESP handles everything automatically. SendGrid, HubSpot, and similar platforms manage IP reputation and basic authentication setup.
But they can’t fix your domain reputation or address list quality issues that damage deliverability systematically.
B2B buyers expect professional communication that reaches their inboxes consistently and reliably.
Stop losing qualified prospects to spam filters
Your email reputation determines whether carefully crafted sequences reach decision-makers or disappear while competitors win deals through consistent inbox placement.
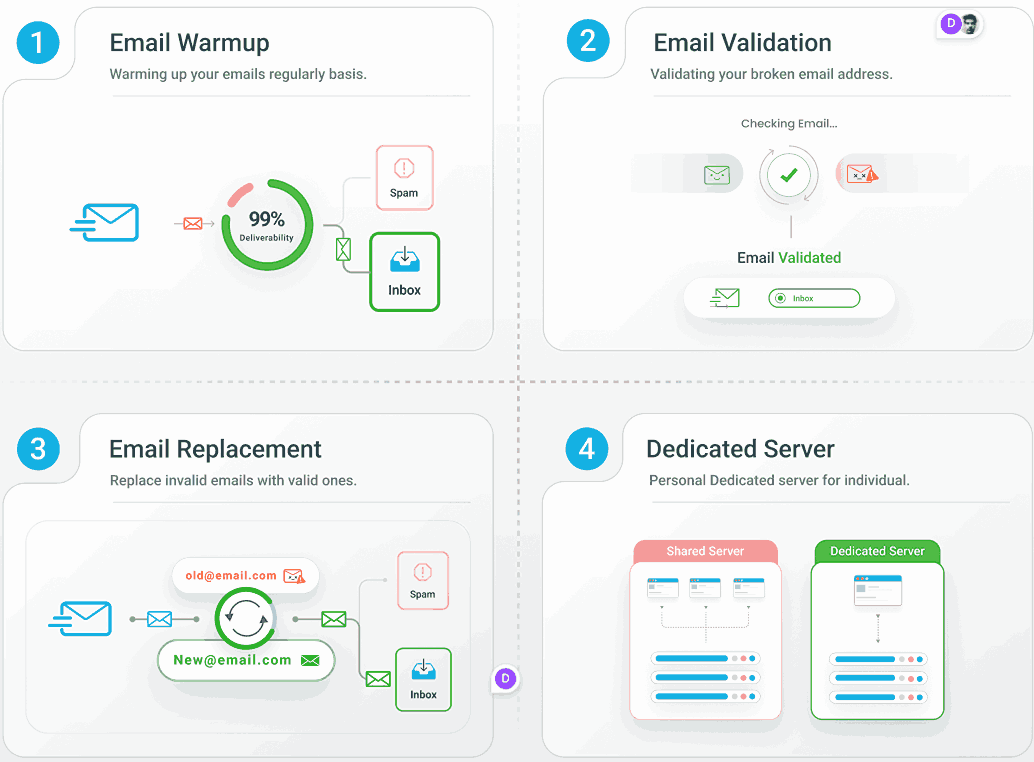
That’s why you need a system that works, and EmailWarmup.com offers:
- Better delivery rates with constant monitoring
- Clean email lists with validation and replacement
- An email warmup that adjusts to how much you send
- Your own IP addresses to protect your sender’s reputation
- Expert help whenever you need it, with unlimited support calls
Stop watching your best emails disappear into spam folders with EmailWarmup.com.
Get started with a free 30-day (no-strings-attached) trial?
Frequently asked questions
Here are some commonly asked questions about email reputation:
Reputation recovery typically requires 4-8 weeks with consistent execution of proper processes. Timeline depends on damage severity, current sending volume, and the precision of your recovery steps. Companies that rush the timeline or skip steps often restart recovery multiple times, extending the overall timeframe significantly.
Stay with shared IPs if you send under 10,000 emails monthly and your ESP manages reputation monitoring effectively. Move to dedicated IPs when you exceed that volume threshold or need complete control over reputation factors. Dedicated IPs require sufficient volume to maintain proper warming — too little volume hurts deliverability performance.
Gmail and Outlook use completely different filtering algorithms with different priorities. Gmail emphasizes engagement signals (opens, clicks, replies) while Outlook focuses more on technical factors like IP reputation and authentication compliance. Your domain might have good engagement metrics but poor technical setup, or vice versa. Test both platforms separately and optimize accordingly.
Switching ESPs changes your IP reputation but doesn’t affect your domain reputation at all. If your domain has reputation damage, it follows you across all platforms and tools. Focus on domain reputation recovery first, then consider ESP changes if IP-level issues persist after domain recovery.
Hard bounces (invalid addresses, blocked domains) directly damage reputation and should be removed immediately from all contact lists. Soft bounces (full mailboxes, temporary server issues) don’t damage reputation as severely but indicate list quality problems if rates consistently exceed 5-10% of your sends.
Use dedicated subdomains (like mail.yourcompany.com) for marketing emails to protect your root domain’s reputation from potential damage. Authenticate both the subdomain and root domain properly through SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. This setup allows you to isolate marketing reputation from corporate email reputation while maintaining brand consistency.
Validate contact lists before every major campaign launch and monthly for ongoing sequence sends. Real-time validation at the point of capture prevents bad addresses from entering your database systems. Batch validation should happen quarterly for your entire database to catch natural degradation over time.
You need SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records configured properly and working together. SPF authorizes sending servers for your domain, DKIM provides digital message signatures, and DMARC instructs ISPs on what to do when authentication fails. All three work together as a complete system — missing any component creates authentication failures that hurt reputation consistently.
Reputation recovery requires a temporary volume reduction to demonstrate improved sending behavior to ISP filtering systems. Maintaining high volumes while attempting recovery sends mixed signals and extends the recovery timeline significantly. The temporary volume reduction leads to better long-term deliverability and higher total delivered volume after recovery completion.


